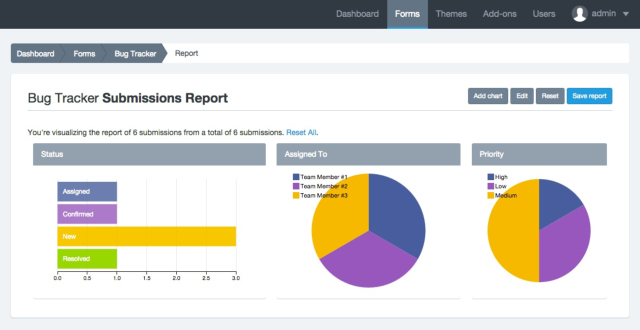
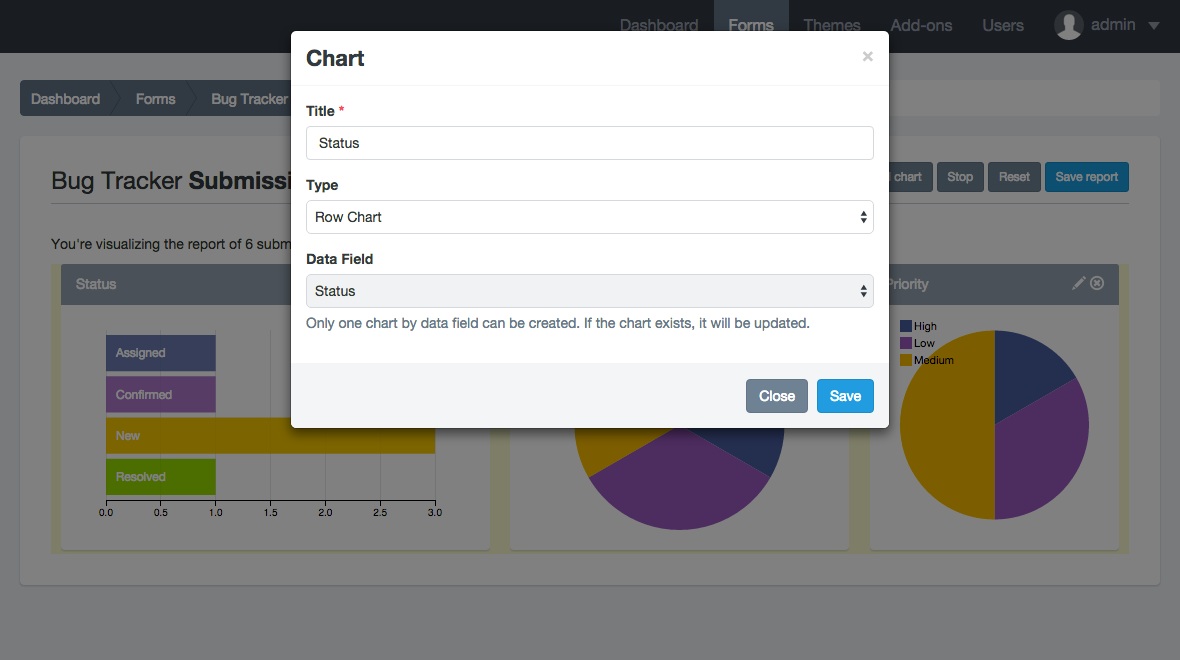
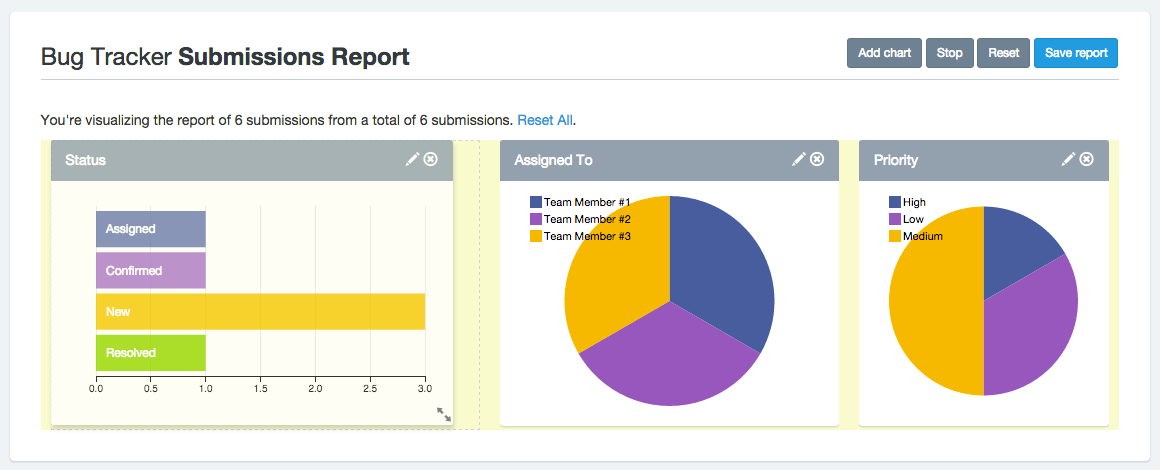
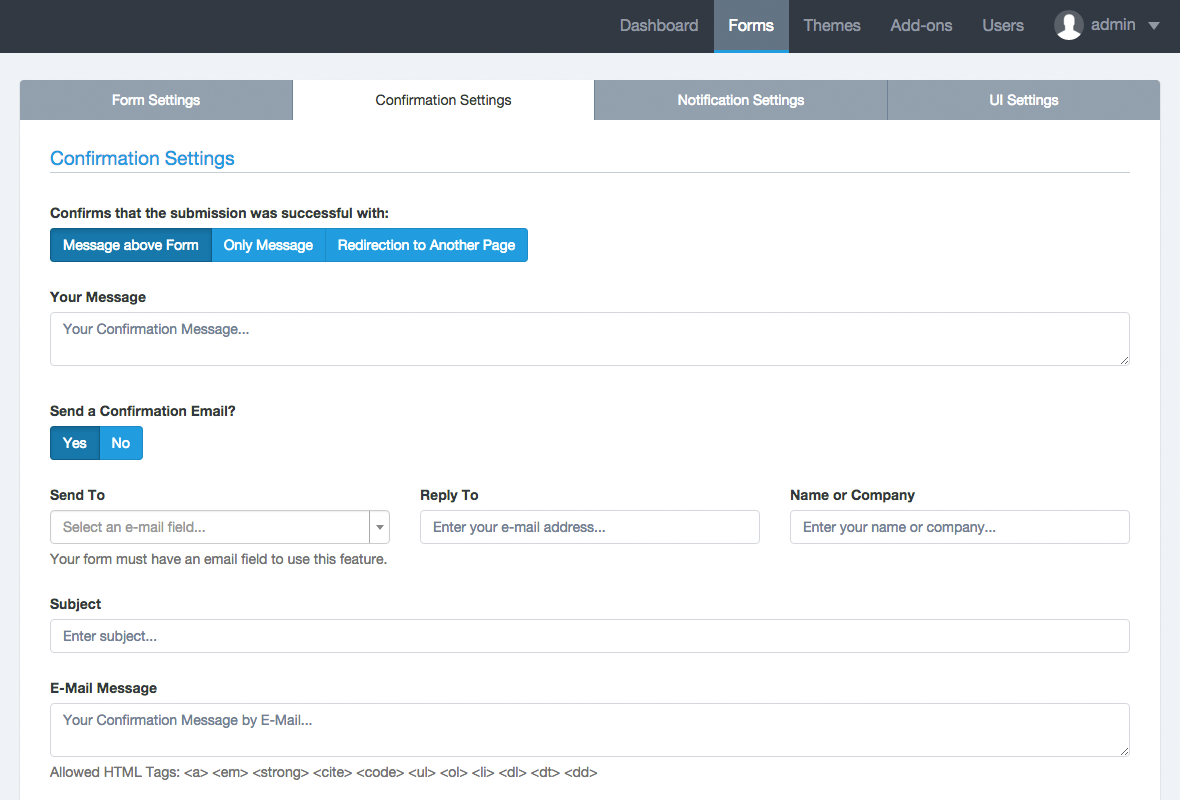
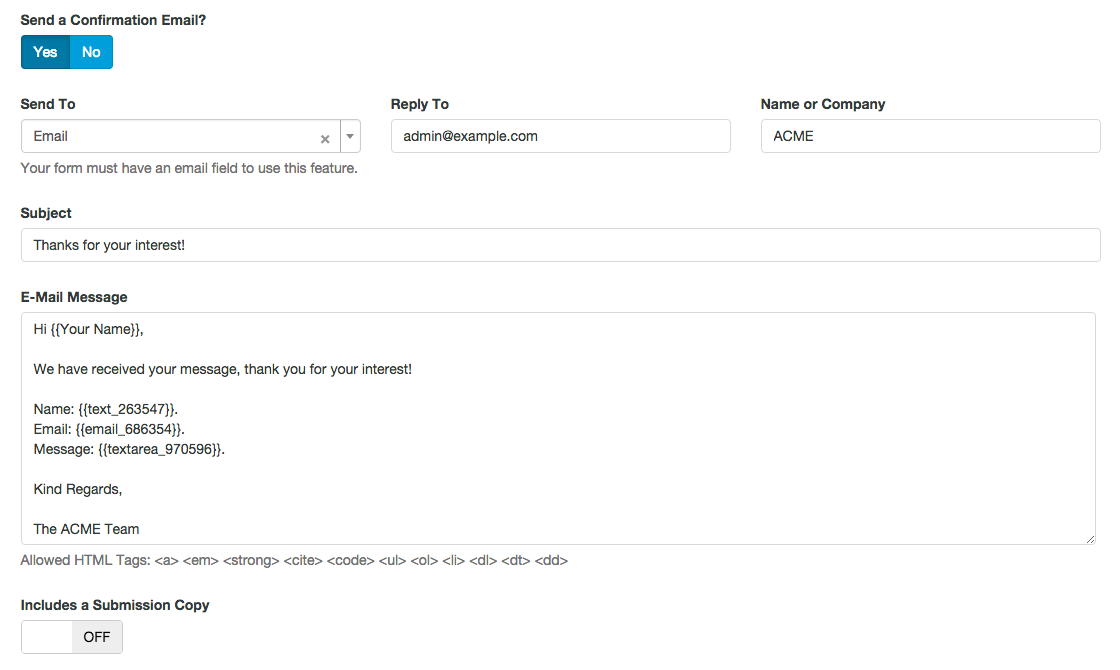
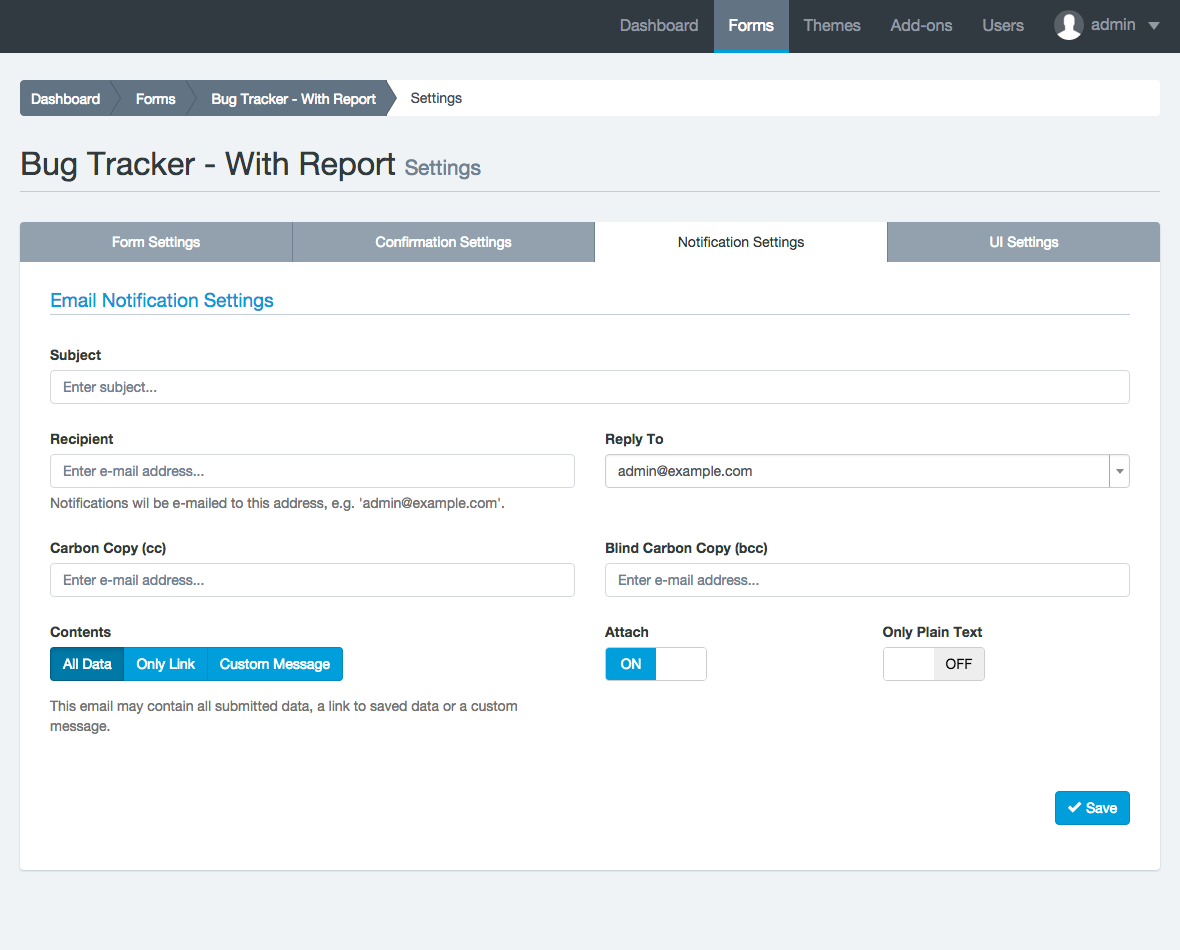
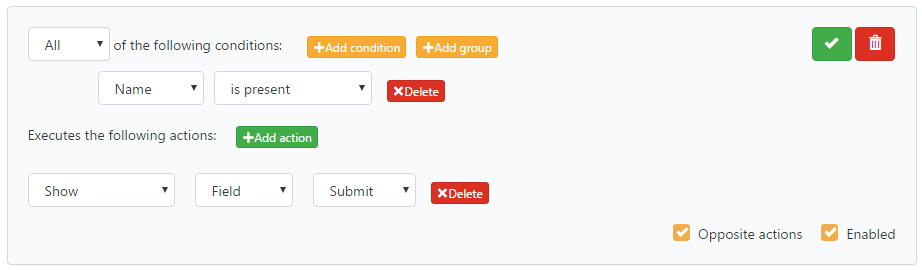
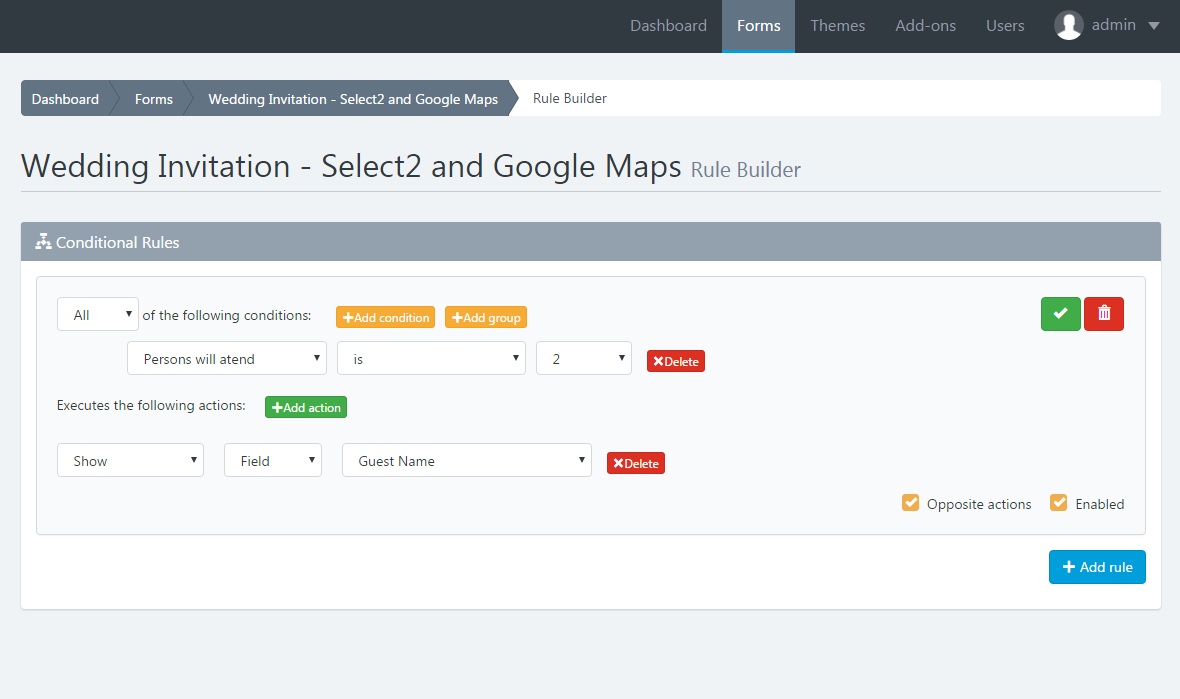
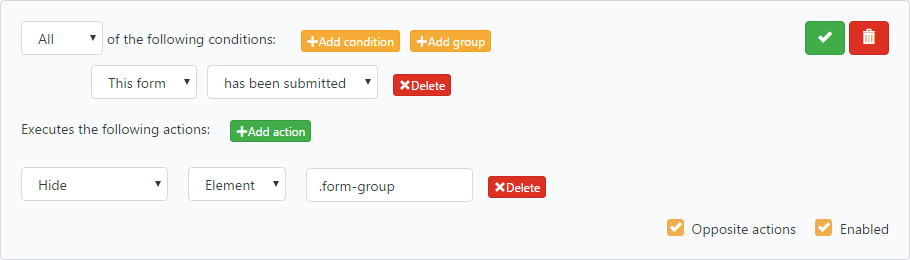
Introduction:
Form Builder is an Docupletionforms key piece. It’s where forms are created and updated. The form builder provides the necessary tools for add and remove fields as other HTML elements.
User Interface:
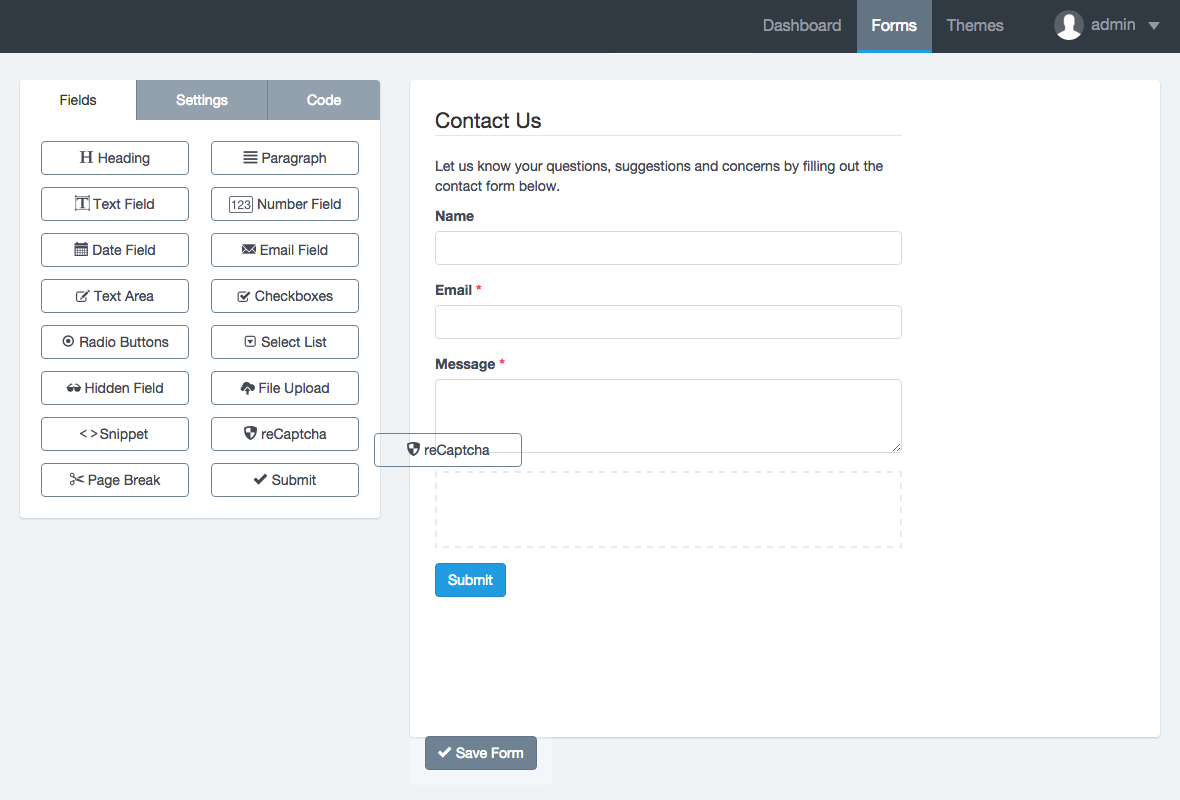
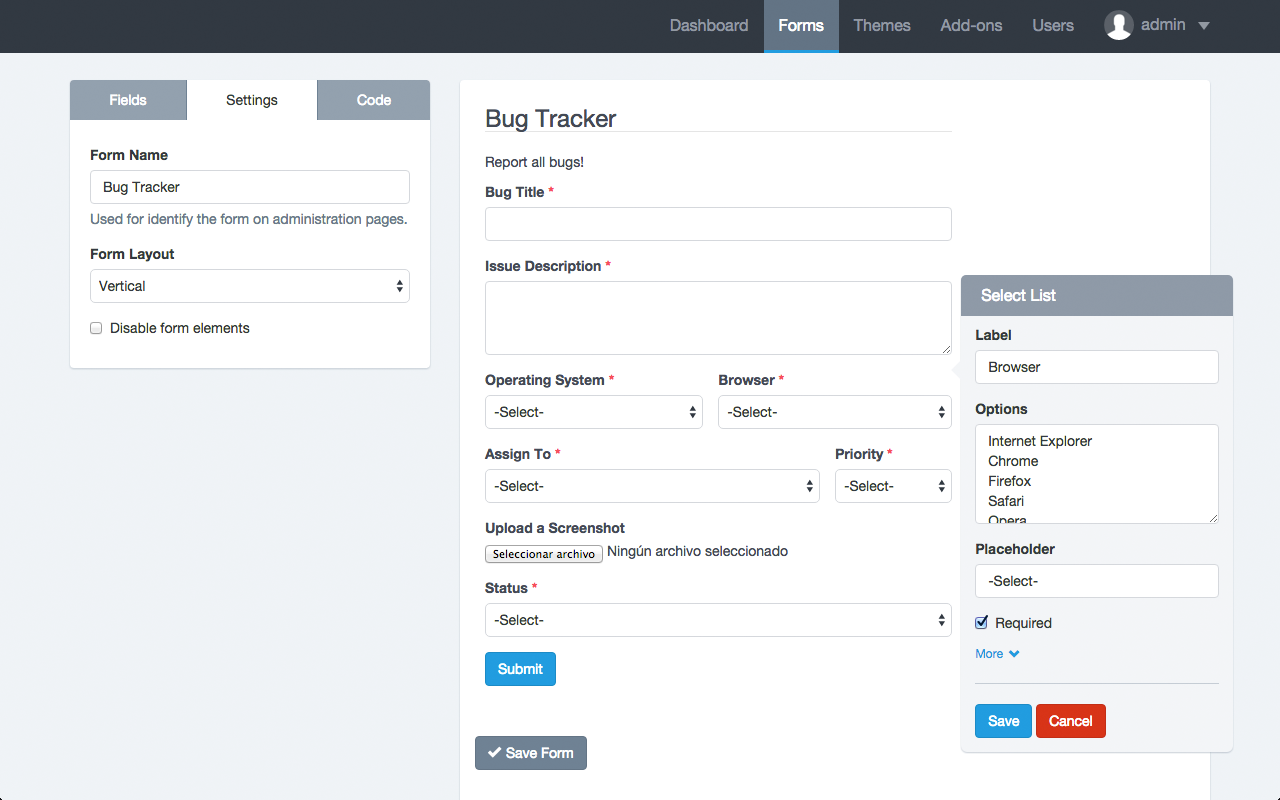
The Form Builder interface is divided into two areas: On the left the form fields and to the right a form preview.
The left area has three tabs:
The tab Fields displays all fields and elements that can be added to the form. Simply drag and drop them to the right area.
The tab Settings let set the form name, the form layout (labels position) and disabling all fields.
The tab Code let see in real time the HTML code that is being generated with the Form Builder. From here you can recognize each element ID to manipulate the Form in a more advanced way.
The right area is the Form Preview from where you can manipulate each of the components.
– Add a field
To add a field:
Click a button on the left panel.
Drag it to the right area.
At the time you enter in the Form Builder’s active area a box will indicate where will be placed the Field.
Once you placed it where you need, drop the button
– Edit a field
To edit a field:
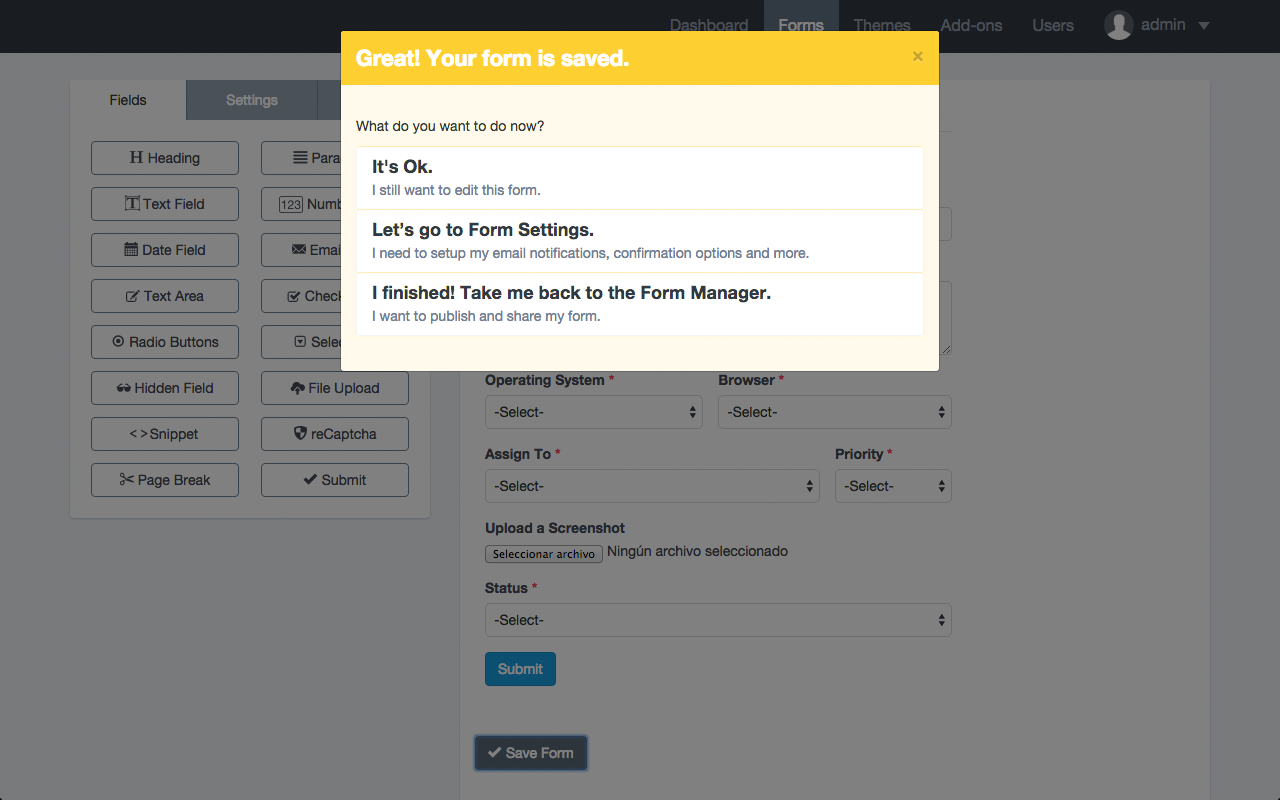
Click on the field to edit and a pop-over will appear with field information
Edit the information according to your requirements.
Click Save.
Note: Pressing ESC will close the popovers.
– Reorder the fields
To reorder a field (component):
Click on a component and hold
Drag the component up or down according to your requirements.
According to where you drag the component, an active zone where the component will be placed will appear.
Once placed in the required place, release the component.
– Delete a field
To delete a field (component):
Click on a component and hold.
Drag it out of the active zone.
Release.
You’ll notice that the component has disappeared.
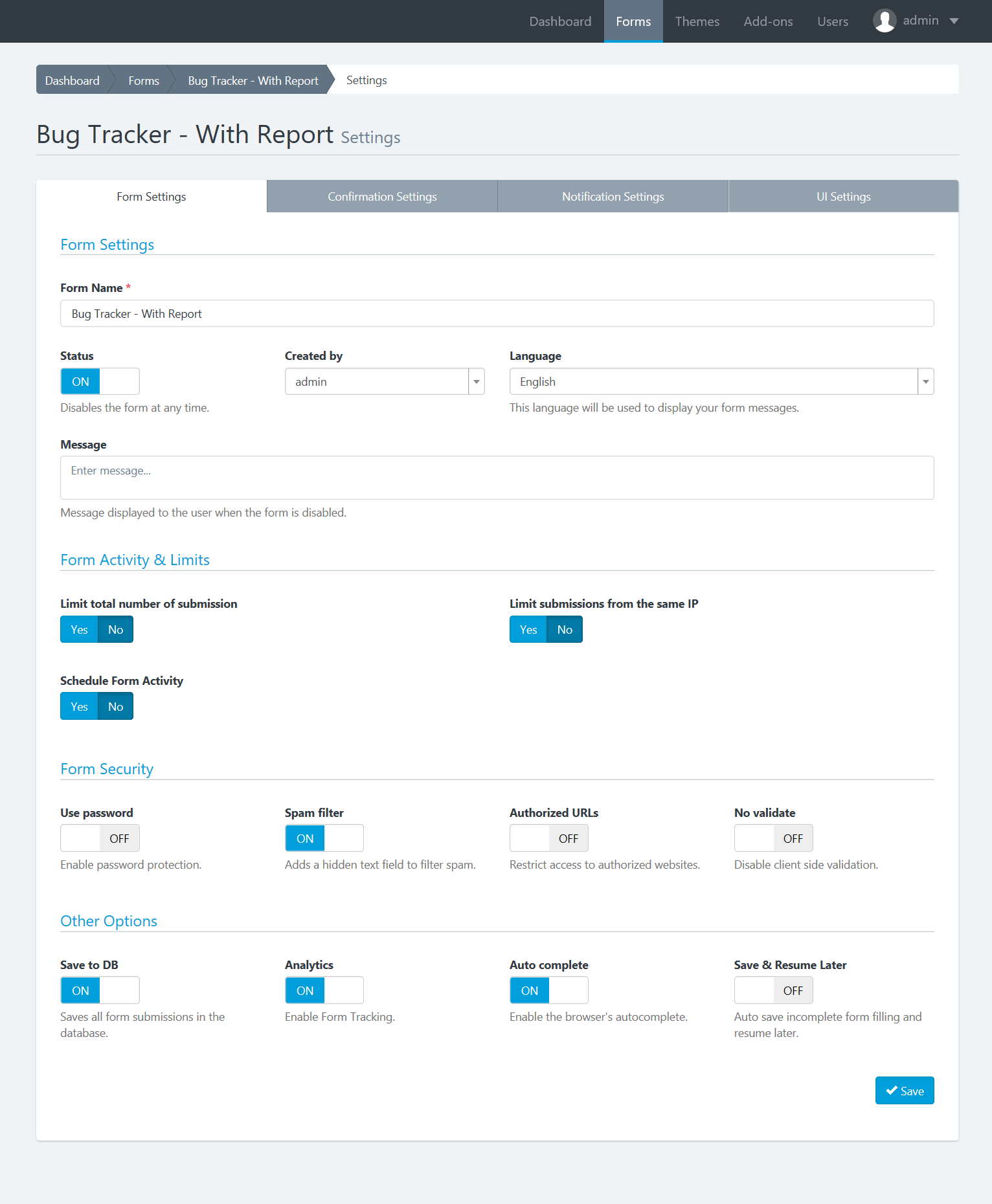
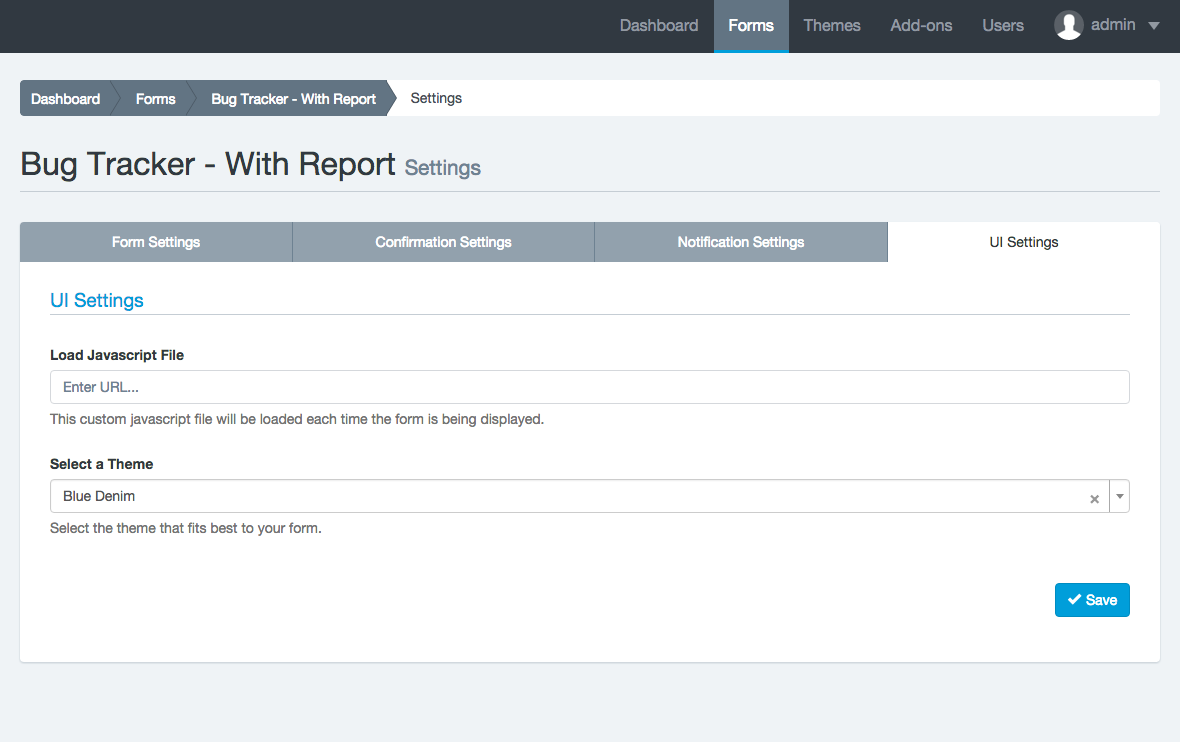
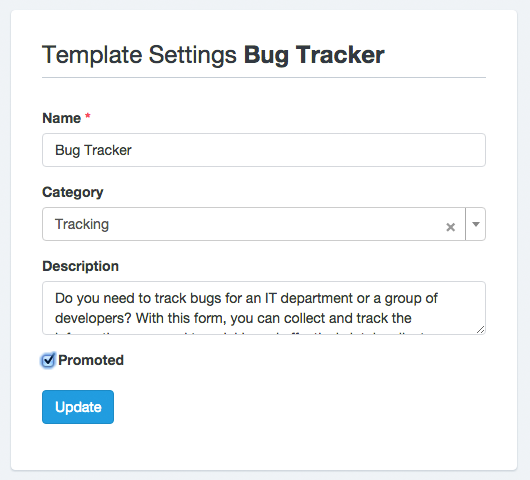
Basic Form Settings
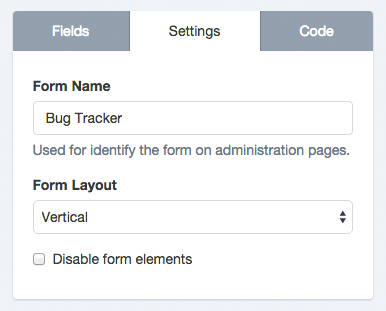
By clicking on the Form Builder’s Settings tab, you will access a very basic version of the form configuration. From here you can:
- Change the form name: The form name is to recognize the Form in the administration pages and is also display as the Form public page title at Docupletionforms.
- Change the form layout: The form layout is based on Bootstrap CSS and is used to locate the labels position on the form.
The Vertical layout displays the field labels above,
The Horizontal layout displays the labels on the field left side, and
The Inline layout hides the labels and displays the fields next to each other. For example, you can use it on a mail registration form, to place an Email field and a button by the side.
- Disable form elements: Let you disable all form fields. It is an advanced option that can be useful if you plan to interact with the form from an external javascript file.
These basic options are intimately related to the form builder. However, you have other Setup options much more advanced that can be accessed from the Form Manager.
Field Settings
Each form field has many Setup options, for example, the label, the default value, the CSS class, etc. To set up a field, go to the preview and click on it.
Setup Options
Next, all the Setup Options are shown in alphabetical order. Not all are in all fields, but if you have any problem, use this list as a reference.
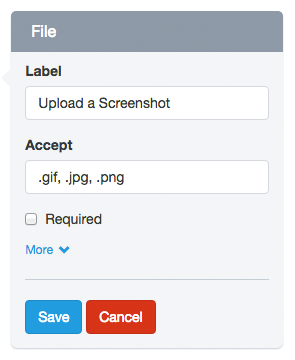
– Accept:
This option is in the File Upload field. With it you can limit the type of files the field can accept. You should consider the following
- You must add the file extensions starting from the dot and separated by commas.
- By default, all files will be validated and will only be accepted image files with extension ‘.gif, .jpg, .png’.
- For example, to accept text files, you can change this option to: ‘.doc, .docx, .txt’.
- If you want to accept all types of files, you must leave this blank.
- This option enables the ‘accept’ attribute from the HTML5 standard, so the field validation is performed both on the client side (browser) and server side.
– Alias:
The Alias option let you send WebHook notifications using the Field Alias instead of the Field Name. For example, we’ll be able to re-send POST data by using “name” or “age” instead of “text_0” or “number_0”.
– Checkbox:
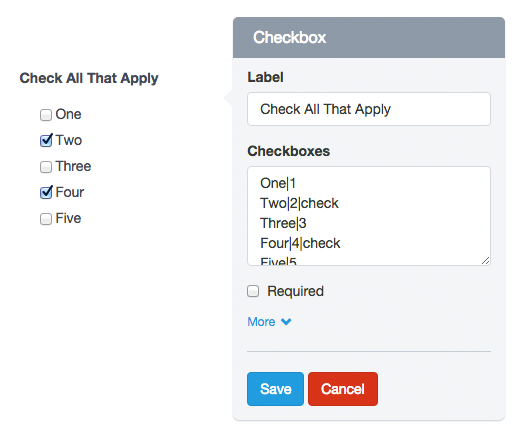
The checkbox option is only in the Checkbox fields and is used to add checkboxes to the component (field).
For example, if you insert in the “Checkbox” option:
One|1
Two|2|check
Three|3
Four|4|check
Five|5
The form preview will show five check boxes with the words One, Two, Three, Four and Five. The option “Two” and “Four” will be checked. And if the user submits the form without making any changes, he will be sending the values: 2,4.
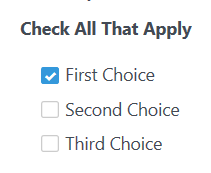
Custom Checkbox
To customize a Checkbox field, you need to add the Container CSS Class: custom-control
– Check DNS:
This option tells the application that in the process of Email Field validation verify that the email domain really exists and has ‘A’ and ‘MX’ records.
Caution! This is an advanced option and should be used with caution. Verification may fail due to a problem with the DNS servers even when is a valid email. By default, it is disabled.
– CSS Class:
Let you add one or more CSS classes to the Form Field.
– Container CSS Class:
Let you add one or more CSS classes to the container of the whole component.
You can create multi-column forms by defining the class col-sm-* (the asterisk represents the number of columns).
For example:
If you want to place two fields in two columns you must do the following:
- Add the container CSS class to the first field: col-sm-6 no-padding-left
- Add the container CSS class to the second field: col-sm-6 no-padding
In this example, we are using the “no-padding” predefined CSS classes to remove the padding that Bootstrap CSS adds to the columns. You can add them or not according to your design. If not, you can add the container CSS class col-sm-12 to the rest of fields, to preserve the same padding on each field.
Important! Don’t forget that if you create more than one row filled with columns, you should add an empty Snippet as separator between each row. You can go to the Bootstrap CSS documentation for more information.
Note:
- By default, all fields except Button, come with the class: form-group. This class cannot be edited.
- By default, the field Button comes with the class: form-action. This class cannot be edited.
Default Value:
You can add a default value to a field. This value appears by default, but the user can modify. If the user submits the form without having modified the default value, this value will be collected to process the submission.
– Disabled:
You can disable a field if you want it to be displayed to the user, but not be edited. (Note that you can also disable a hidden field). Unlike the Read Only option, a disabled field is not sent to the server. That is, the information stored in a disabled field is not received and therefore not appear on the Submissions Manager.
– Field Size:
A Text Area field allows its size configuration. The size must be an integer and indicates the number of rows displayed or, in other words, the field height. By default is 3.
– Help Text:
The text you type here will appear below the field and is often used to give the users instructions on what to put in it.
– Inline:
The Inline option is in the Checkbox fields and Radio Buttons and is used to change the vertical position of the checkboxes or radio buttons for a horizontal position.
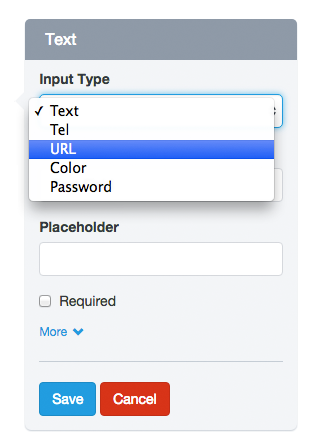
– Input Type:
Many fields allow you to change the Input Type to specify the type of data you will receive. For example, a Text Field can have an Input Type “URL”, to ensure that the text you type here is an absolute URL that starts with the letters ‘http’.
– Integer Only:
You can activate this option if you want the value of this field to be only an integer. If the user enters a floating point number, the Form would not be processed and instead a validation error appears.
– Integer Pattern:
Is an advanced option of the Number Field that allows you to customize the regular expression that accepts only integer numbers (0-9) and will be used in the Form Validation process. The regular expression used by default is ‘/^\s[+-]?\d+\s$/’;
– Label
It is the most common way to inform the user the value he must enter in the field. Generally it is shown at the top of the field, but you can modify this position by changing the form layout.
– Label CSS Class:
Let you add one or more CSS classes to the label. Keep in mind that if you want to hide a label, you can add the Bootstrap 3 css class ‘sr-only’.
Note: By default all fields come with the CSS class: control-label. It is recommended not to remove it.
– Max date:
You can define a date as the maximum date to be taken into account in the validating field process. If the user enters an later date, the form will not be sent and instead, a validation error will appear. If this option is not defined, this limitation will not exist.
Important! The date must keep the following format: yyyy-mm-dd (HTML5 standard format)
– Max number:
You can define an integer or floating-point number as the maximum number to be taken into account in the validating field process. If the user enters a larger number, the form will not be sent and instead, a validation error will appear. If this option is not defined, this limitation will not exist.
– Max Size:
You can define an integer number as the maximum size that will be taken into account in the process of validating the field. If the user uploads a file with a size larger than the one you defined, the form will not be sent and instead, a validation error appears. If this option is not defined, this limitation will not exist.
The integer number represents the number of bytes allowed. For example, Max Size: 10311680 (resulting from the multiplication of 1024 x 1024 x 5), the maximum file size should be 5MB.
– Min date:
You can define a date as the minimum date to be taken into account in the validating field process. If the user enters a earlier date, the form will not be sent and instead, a validation error will appear. If this option is not defined, this limitation will not exist.
Important! The date must keep the following format: yyyy-mm-dd (HTML5 standard format)
– Min number:
You can define an integer or floating-point number as the minimum number to be taken into account in the validating field process. If the user enters a lower number, the form will not be sent and instead, a validation error will appear. If this option is not defined, this limitation will not exist.
– Min Size:
You can define an integer number as the minimum size to be taken into account in the process of validating the field. If the user uploads a file with a smaller size than the one you have defined, the form will not be sent and, instead, a validation error appears. If this option is not defined, this limitation will not exist.
The integer number represents the number of bytes allowed. For example, Min Size: 10311680 (resulting from the multiplication of 1024 x 1024 x 5), the minimum file size should be 5MB.
– Multiple:
This option indicates that the user can enter multiple values. You can find this option in the Email and Select List fields:
- If Multiple option is enabled on an Email field, you can add several valid email addresses separated by commas. For example: ‘name@example.com,name2@example.com’.
- If Multiple option is enabled on a Select List field, you can select several options. The collected information will have a comma-separated format. For example: ‘Option One, Option Two’.
– Number Pattern:
Is an advanced option of the Number Field that allows you to customize the regular expression that accepts any number and will be used in the Form Validation process. The regular expression used by default match with a floating point number and optionally an exponent part (eg -1.23e-10): ‘/^\s[-+]?[0-9].?[0-9]+([eE][-+]?[0-9]+)?\s*$/’.
– Options:
The Options option is only in the Select List fields and are used to add selection options to the component.
For example, if you enter in the Options field of the pop-up Form:
One|1
Two|2|select
Three|3
Four|4
Five|5
The Form Preview will show a box with the text “Two”. And if the user submits the form without making any changes, he will be sending the value: 2.
– Pattern
It is an advanced option and allows you to add a regular expression to the field to be used in the Form Validation process. If the value sent by the user does not match this pattern, the form will not be processed and instead a validation error appears.
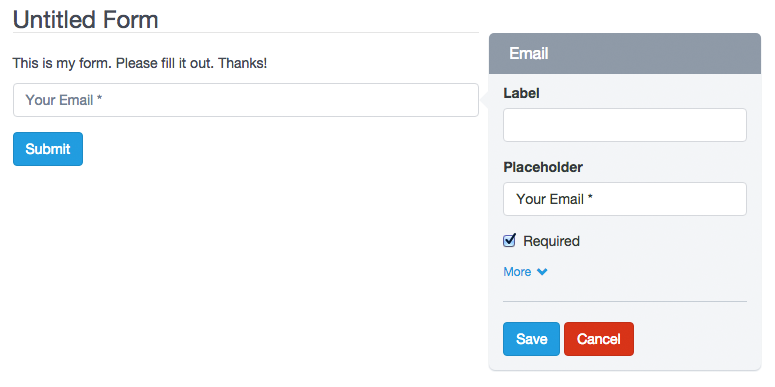
– Placeholder
It is the alternative way of describing the value that the user must enter in the field. By default, the placeholder appears in the field until the user start to enter data.
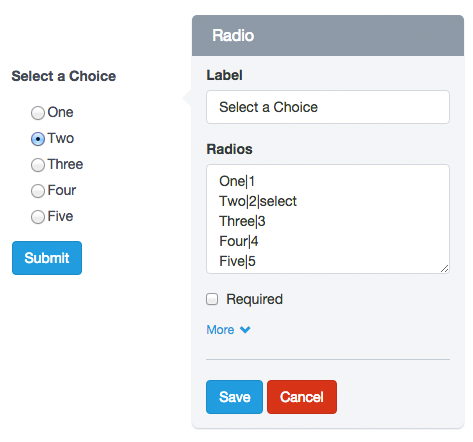
–Radios:
The Radios option is only in the Radio Buttons fields and is used to add radio buttons to the component.
For example, if you enter in the Radios field of the pop-up Form:
One|1
Two|2|select
Three|3
Four|4
Five|5
The Form Preview will show five radio buttons with the words: One, Two, Three, Four and Five. The option Two would be selected. And if the user submits the form without making any changes, he will be sending the value: 2
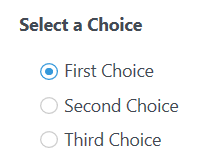
Custom Radio Button
To customize a Radio Button field, you need to add the Container CSS Class: custom-control
– Read Only:
When you enable this option, the field will be displayed to the user but he cannot edit. The information in a Read Only field is received and validated by the server when the Form is submitted. It will also be collected by the Submission Manager.
– Required
This property allows you to ensure that the user complete a specific field before sending the form. If the user submits the form with an empty required field, the form is not processed and instead an error message is displayed. By default, the required fields labels have a red asterisk on the right.
– Step number:
With this option, you can set the HTML5 ‘step’ attribute of the Number and Date fields. The ‘step’ attribute specifies the valid number to be use as an interval when changing the values of this field using the browser controllers. Modern browsers recognize this attribute.
Important! If the Number field has the ‘Integer Only’ option enabled is recommended to set your ‘Step number’ to 1.
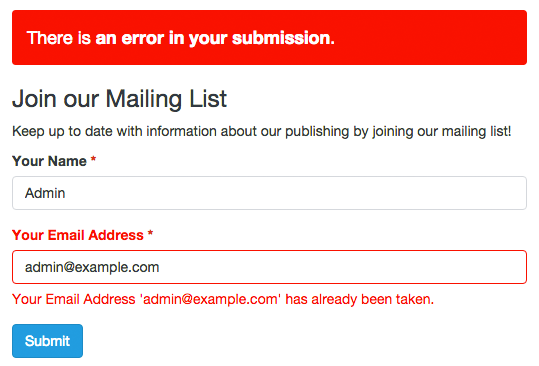
– Unique:
This option allows you to check that the information entered into this field is unique and has not been submitted previously. Useful for mailing lists and registration forms, where preventing the users from entering the same information more than once is often needed.
– Unique:
Field Types
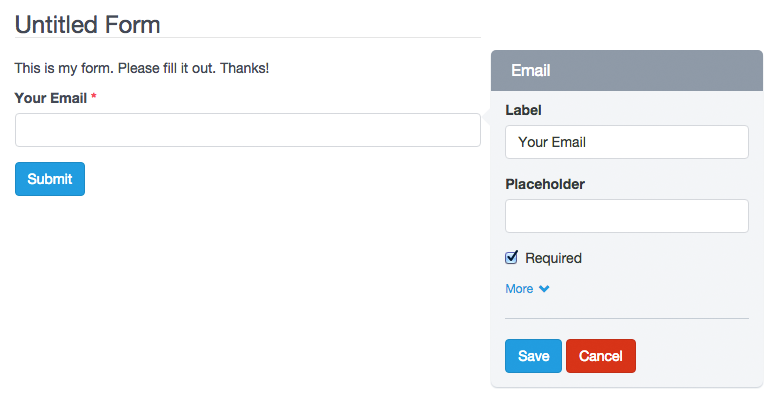
– Heading
Headings are used to mark Form sections, also as to give it a title. For example, when you enter the Form Builder to create one, you will see a heading (h3) with the text “Untitled Form”. To modify this text, just click on it. Immediately a form will appear with all the options to customize it.
– Paragraph
Paragraphs are components used for fleshing out a form. For example, you can use them to invite your users to fill out the form or to give directions. When you enter to the Forms Builder to create one, you will see a paragraph with the text “This is my form. Please fill it out. Thanks!” To modify this text, simply click on it. Immediately a form will appear with all the options to customize it.
– Text Field
A text field is a component that allows you to write only one line of text. Web browsers consider the text field as the standard default field from others more specialized such as URL or color. The text field can have five different input types, each of which is used to validate data differently. The five types are:
- Text: This is the default type for this component. And it is one that is commonly used in forms, because it does not offer any validation and will accept all data sent by the user. If the browser does not recognize any other type, such field will be displayed instead.
- Url: This type was introduced by HTML5 and now modern browsers accept it. Use the URL type if you want to collect absolute URLs that starts with ‘http’.
- Color: This type was introduced by HTML5 and modern browsers that accept it, displays an automatically color palette when you click on it. Use the Color type if you want the collected data to be the hexadecimal value of a color, starting with a ‘#’ sign. For example, ‘#FFFFFF’.
- Tel: This type was introduced by HTML5 and now modern browsers accept it. Use this type if the data to collect is a phone number.
- Password: All browsers recognize this type of entry. Use this entry type if you want the user to enter data not shown on screen. Note that Docupletionforms is not meant to store passwords, mainly because the data is stored as plain text. If required, use this input type with caution.
– Number Field
A number field is a component used to collect numbers as content. Following the HTML5 standard, this component can be of 2 types:
- Number: This is the type that should be used when you want the user to type the number. For example, you may ask: “How old are you?” If the user enters ‘Five years’, they are notified that they must write only numbers: 5, in this case.
- Range: This type of entry is also used to collect numerical data, but unlike Number, modern browsers display a slider the user can use to enter his data. For example, you can ask “From 1 to 10, how good are you at math?” Depending on how you drag the slider, the value will be higher or lower.
Unlike Text components, Number components offer many different validation options. For example, Integer Only indicate that the field must collect only numerical integers data: Decimals are not accepted! You can also set the minimum and maximum number to be entered and more. All these options follow the HTML5 standard and are also validated on the server.
– Date Field
A date field is a component used to collect valid dates. Date fields were introduced by HTML5 and modern browsers that recognize them display a calendar by clicking on the field. This component can have 5 different types of input:
- Date: The input type to use if you want to collect dates. You must have the format: yyyy-mm-dd.
DateTime-Local: The input type to use if you want to collect dates and times. The collected data will have the standard ISO format: yyyy-mm-ddThh:mm:ss.
- Time: The input type to use if you want to collect times in the format: hh:mm:ss.
- Month: This type of entry is supported by modern browsers and should be used if you want the user to select the month or month and year. The input format is yyyy-mm.
- Week: This type of entry is supported by modern browsers and should be used if you want the user to select the week of the year in numerical format.
Note: Indeed some modern browsers don’t yet show the Datepicker when the field is a date. But, in the future all of them will do. For now, browsers that don’t support it are Safari, Firefox and previous versions of IE. For these cases, we can use a jQuery UI Datepicker widget as fallback.
– Email Field
An email field is used to collect valid emails. By default it validates that the text contains a ‘@’ and ‘.’ plus two or more characters for the e-mail domain. In addition, you must use this field to send notifications that have your users mails as senders (Reply-To).
An advanced option of this field is the ability to verify the mail DNS to confirm that the domain really exists and has an A and MX record. Care should be taken that this validation can fail due to problems with the DNS servers even when mail is valid. By default, this option is disabled.
– Text Area
A text area is a component that allows you to collect multiple lines of text, with multiples paragraphs. It is a suitable field if you want users to draft a comprehensive text. Also, you can change some settings. For example, you can change the height of the text area, to display more space to your users. To do this, click on the text area and change the size of the field that by default is 3.
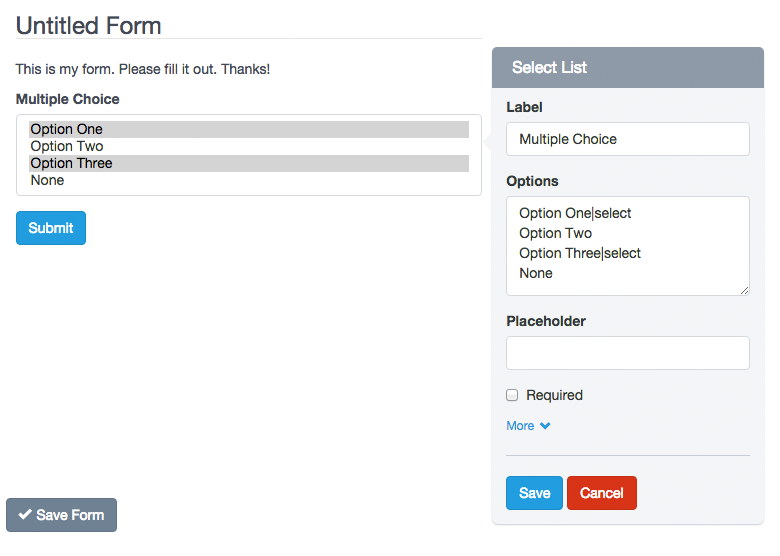
– Checkbox
Checkbox is a component that adds check boxes to the form. This component provides an option list with a checkbox next, so your users can check all, some or none. Its use is recommended when you ask for several answers, for example: Which of the followings are fruits?
To add, edit and delete options, you must click on the component. Then a form appears with the “Checkbox” field. Note that each line of this field represents a different option. And each line can be composed of three parts, separated by a vertical bar or pipe line. The format should be as follows: Label|Value|check. The second and third part of this format is optional.
For example, if you enter in the field “Checkbox” of the pop-up Form:
One|1
Two|2|check
Three|3
Four|4|check
Five|5
The Form Preview will show 5 check boxes with the words One, Two, Three, Four and Five. The “Two” and “Four” option will be selected. And if the user submits the form without making any changes, it will be sending the values: 2,4.
Also, since version 1.3 you can add pictures or icons to the checkboxes to give a more dynamic touch to your forms.
To insert a picture on a checkbox label you must add the image url as the third setting parameter of the checkbox. For example, if we set up our component as:
One
Two|2
Three|3|check
Four|4|http://example.com/image-4.jpg
Five|5|http://example.com/image-5.jpg|check
We’ll be creating five checkboxes:
One: Creates a checkbox with the value: ‘One’ and the label: ‘One’
Two|2: Creates a checkbox with the value: ‘2’ and the label: ‘Two’
Three|3|check: Creates a checkbox with the value: ‘3’, the label: ‘Three’ and will be checked by default.
Four|4|http://example.com/image-4.jpg: Creates a checkbox with the value: ‘4’, the label: ‘Four’ and the image will appear next to the checkbox.
Five|5|http://example.com/image-5.jpg|check: Creates a checkbox with the value: ‘5’, the label: ‘Five’ and the image will appear next to the checkbox and will be checked by default.
To add icons instead of images, you should only replace the images URLs by the icons’ CSS classes. For example: glyphicon glyphicon-user, will display the user icon. Keep in mind that by default, the application has the Glyphicons Pro set of icons; however, you can use other icons like Font Awesome or DevIcons. For this, you just have to add the fonts to the CSS theme of your form.
Important: To add an image or icon to the checkbox setup, you must have the first two parameters, even if they are the same.
Note: Remember that you can display your checkboxes horizontally by activating the ‘inline’ attribute.
– Radio Button
Radio Button is a component that lets you add a group of radio buttons to the form. This component gives users a list of choices, but they must select only one of them. For example: What is your favorite color?
To add, edit and delete options, you must click on the component. Then a form appears with the “Radio” field. Note that each line of this field represents a different option. And each line can be composed of three parts, separated by a vertical bar or pipe line. The format should be as follows: Label|Value|select. The second and third part of this format is optional.
For example, if you enter in the field “Radio” of the pop-up Form:
One|1
Two|2|select
Three|3
Four|4
Five|5
The Form Preview will show 5 check boxes with the words One, Two, Three, Four and Five. The “Two” option will be selected. And if the user submits the form without making any changes, it will be sending the value: 2.
Also, since version 1.3 you can add pictures or icons to the radio buttons to give a more dynamic touch to your forms.
To insert a picture on a radio button label you must add the image url as the third setting parameter of the radio button. For example, if we set up our component as:
One
Two|2
Three|3|select
Four|4|http://example.com/image-4.jpg
Five|5|http://example.com/image-5.jpg|select
We’ll be creating five radio buttons:
One: Creates a radio button with the value: ‘One’ and the label: ‘One’
Two|2: Creates a radio button with the value: ‘2’ and the label: ‘Two’
Three|3|select: Creates a radio button with the value: ‘3’, the label: ‘Three’ and will be selected by default.
Four|4|http://example.com/image-4.jpg: Creates a radio button with the value: ‘4’, the label: ‘Four’ and the image will appear next to the radio button.
Five|5|http://example.com/image-5.jpg|select: Creates a radio button with the value: ‘5’, the label: ‘Five’ and the image will appear next to the radio button and will be selected by default.
To add icons instead of images, you should only replace the images URLs by the icons’ CSS classes. For example: glyphicon glyphicon-user, will display the user icon. Keep in mind that by default, the application has the Glyphicons Pro set of icons; however, you can use other icons like Font Awesome or DevIcons. For this, you just have to add the fonts to the CSS theme of your form.
Important: To add an image or icon to the radio button setup, you must have the first two parameters, even if they are the same.
Note: Remember that you can display your radio button horizontally by activating the ‘inline’ attribute.
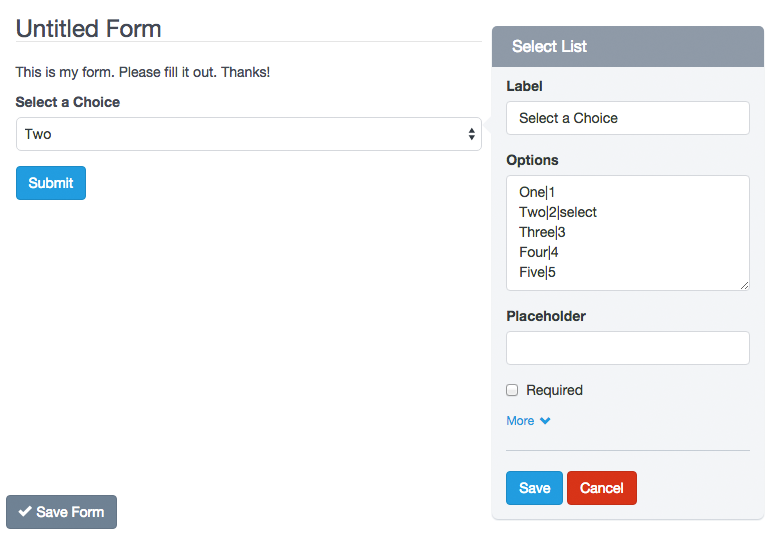
– Select List
A Select List is a drop-down menu that allows the user to select one or several options, depending on the configuration you choose. The main difference with the Radio Button component is that you can add a lot of options without changing its size. So its use is recommended when there are plenty of options for example: Select your country of origin?
To add, edit and delete options, you must click on the component. Then a form appears with the “Options” field. Note that each line of this field represents a different option. And each line can be composed of three parts, separated by a vertical bar or pipe line. The format should be as follows: Label|Value|select. The second and third part of this format is optional.
For example, if you enter in the field “Options” of the pop-up Form:
One|1
Two|2|select
Three|3
Four|4
Five|5
The Form Preview will show a box with the text “Two”. And if the user submits the form without making any changes, it will be sending the value: 2.
– Hidden Field
By adding a hidden field to the form, this will not be shown on the form. However, hidden fields are useful for mathematical calculations or send default values without changing the form interface.
Note: You can add a label to a hidden field to work in a more comfortable way in the Form administration, for example to create conditional rules using this field.
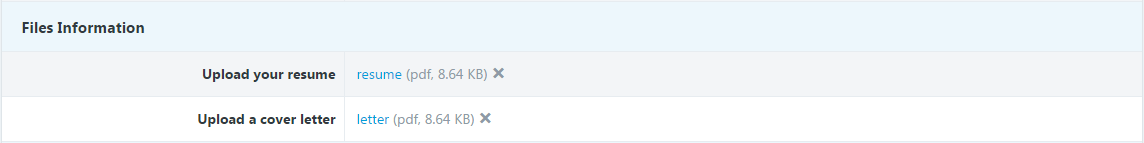
– File Upload
The File Upload field is a component that enables users to attach files in the form submission. Once sent, the files will appear in the detailed submission information. There are two details that must take into account:
- Allowed file types: You can limit the types of files that can be uploaded in each file field. By default, allowed file types for picture are: ‘.gif, .jpg, .png’. To modify the allowed file type, you must click on the component and on the ‘Accept’ form field that appears, change file extensions allowed, eg, ‘.doc, .pdf, .txt’ to accept text files.
- Size limitations: You can limit the file size as define a minimum or maximum size for each field. To modify the allowed file size, click the component and then expand the pop-up form by clicking on the ‘More’ link. Then locate the Minimum and Maximum Size fields and enter the digit that represents the number of bytes allowed. For example, Max Size: 10311680 (resulting from the multiplication of 1024 x 1024 x 5 = 5MB).
– Snippet
The Snippet field is an advanced use component and allows users to add HTML code. The code inserted will be displayed on the form as such. However, care must be taken to introduce a valid html code, otherwise the Form Builder does not save the form and, instead, displays a error message indicating the line of code where the error was made. For example, a common mistake is to add more of one HTML element with the same ID.
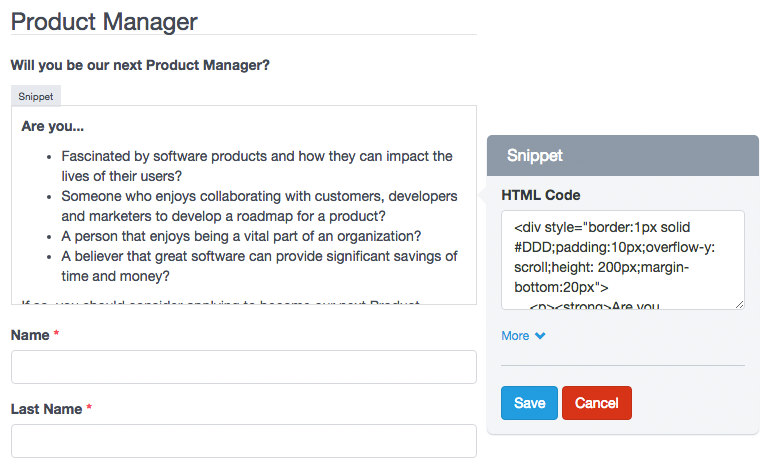
Note: Although you can add CSS and JavaScript code in a form. It is not recommended to do so, in these cases you can create a CSS Theme and/or Load external javascript file. Remember that the form you created is also displayed in the Submission Manager and its code could be incompatible.
– reCaptcha
The reCaptcha field is an advanced component that allows you to use Google technology to verify that users are not bots and/or spammers. You can modify the reCAPTCHA configuration, like changing the theme color, type of captcha and size. A detail to keep in mind is that you can only add a reCaptcha component per Form.
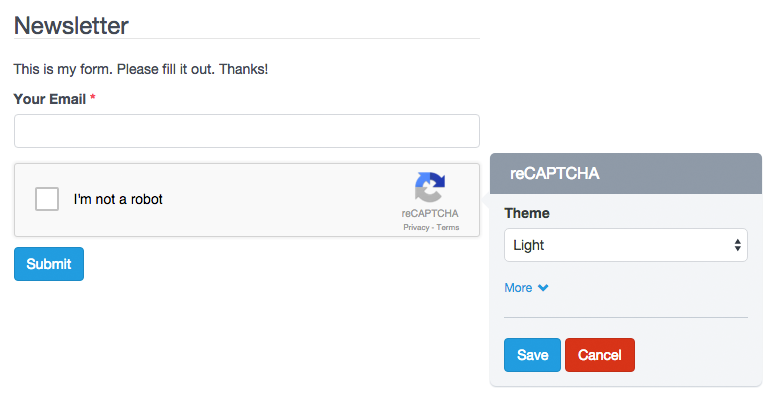
Important! Before adding the reCAPTCHA component to your Form, you must first add reCAPTCHA keys in the site configuration. Otherwise, reCAPTCHA will not operate. If you created the form before adding the keys, you must update the form.
– Page Break
The Page break field is an advanced component that allows you to create multi-step or multi-page forms. For each page break created you will add a new page. In addition, a header will be displayed above the form to let users know in which step they are and how many steps must follow to submit the form. There are two details that must take into account:
- The Page Break component adds two buttons to allow Form Navigation. You can customize the text on the button ‘Next’ or ‘Previous’ by clicking on the component.
- Form Steps: Shown above form and may be modified as follows.
- Click Form Steps to check its settings. You can change the titles of each step in the field Form Steps. Each line matches a title.
- You can specify to display only the titles or steps (numbers).
- You can change the step numbers by glyphicons icons. To use Glyphicons in stages, you should add to each line of the Steps fields, a vertical bar or pipe line followed by ‘icon-[name of icon]’. For example, if I want to replace the number 1, I write it in the first line of Steps: ‘Untitled Step|icon-user’. Go to Glyphicons to view the name of the icons you can use.
- You can change the design of the steps for a progress bar indicating the percentage that has been achieved.
- Finally, you can hide the Form Steps by checking the ‘No Form Steps’ option.
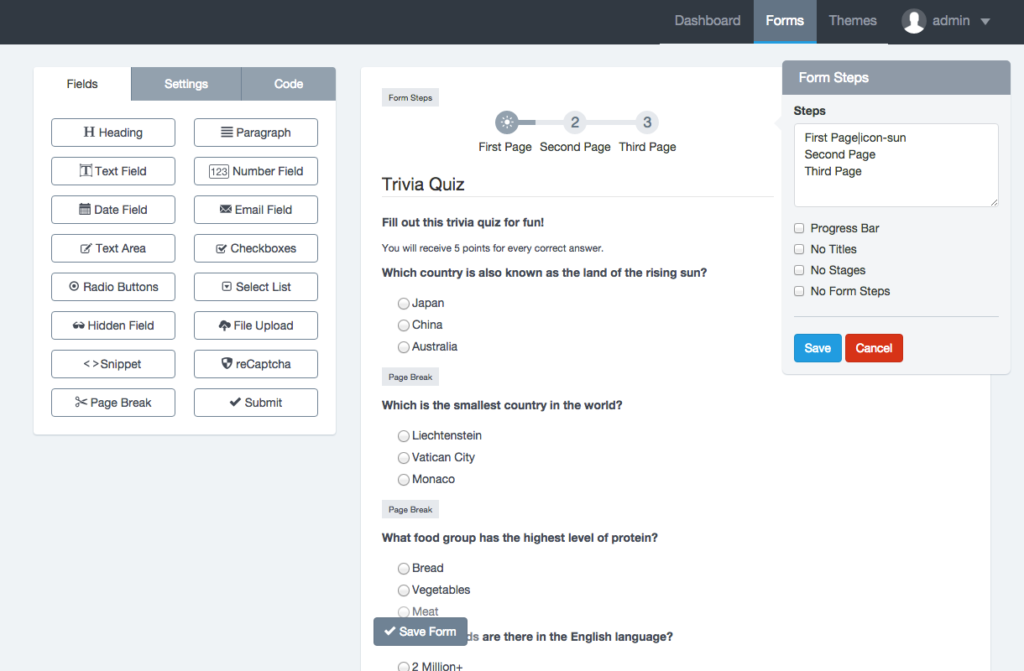
-Button
The button field is a component that allows you to send the forms. While it is normal to add one button per form, nothing prevents you to add more, for example at the beginning and end of the form. This component can be of 3 types:
- Submit: To submit the form. It is selected by default.
- Reset: To reset the form to their default values.
- Image: Displays an image on the button and like Submit is used to submit the form. If you use this type of button you need to add the URL of the image and also remove the CSS class.
- Button: This type doesn’t send the form, but it can be used to interact with the fields via javascript.
You can add an icon to the buttons type ‘Submit’, ‘Reset’ and ‘Button’, writing in the attribute ‘Button Text’ the icon label. For example:
<span class=”glyphicon glyphicon-shopping-cart”></span> Buy Now!
It will display your button with a nice icon at the beginning:
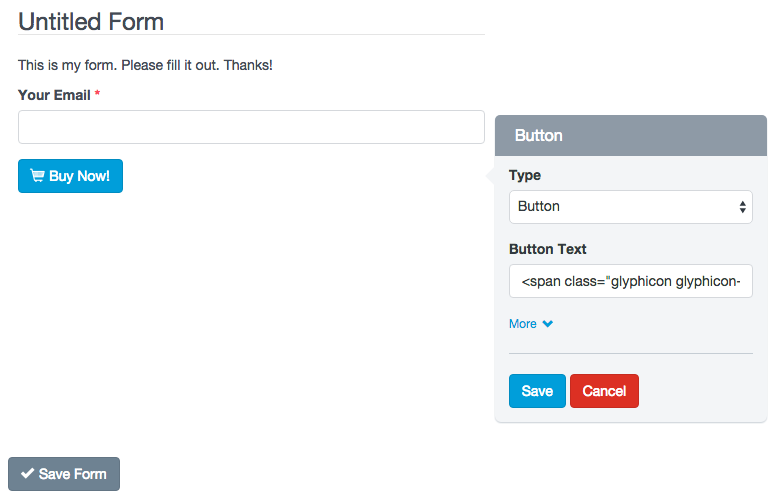
Note: The CSS class: ‘btn btn-primary’ add the default design to the button. Go to Bootstrap CSS for more information.
Field Validation
A very important point to consider is the field validation that runs when users submit a form.
Field validation is the process by which it is verified that the data submitted by users meet certain requirements. For example, a Date Field requires that the value sent to the server has the following format yyyy-mm-dd. Validation ensures that this happens.
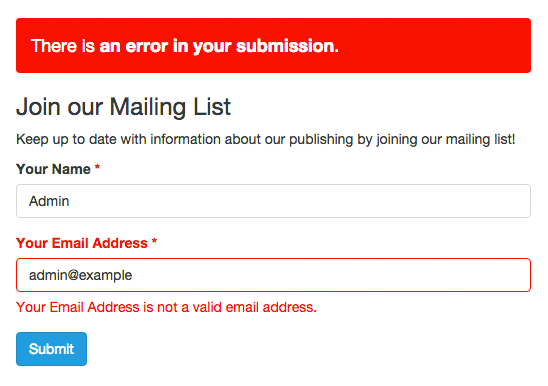
You should note that Form Builder works with standard HTML5 fields, so you can always go to HTML5 documentation for more information. In addition to validation by type, fields may have other requirements, such as ‘Required’ and ‘Unique’.
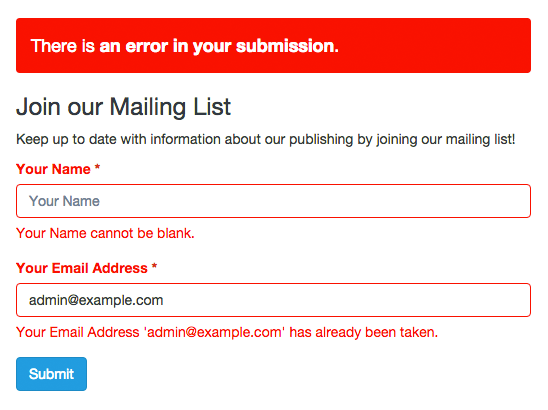
Many of these requirements are validated at the client, by the browser; but they are all validated on the server, by Our Form Builder.


 DocupletionForms.com is a FREE Contact Form Program with a $5 Data-Merge element that can be added.
DocupletionForms.com is a FREE Contact Form Program with a $5 Data-Merge element that can be added.